
Do people with albinism have pink eyes?
It is a very common misunderstanding that people with albinism have pink or red eyes. In fact their irises vary in colour from light gray or violet, to the most common blue and in some cases even brown. The pink and red colour may occur when light is reflected off the back of the eye similar to the way a camera flashes and produce red eyes.
If albinism is genetic will all my children have albinism?
To be born with albinism, a baby must inherit the recessive “albinism” gene from both its parents (they are both carriers of the gene). Carriers usually have one dominant gene and one “albinism” gene and show no symptoms of albinism, as the dominant gene results in normal pigment levels being formed. When both parents are carrying the “albinism” gene, they have a one in four chance in each pregnancy that their recessive “albinism” genes will pair and the child will have Albinism.
Is there a “cure” for albinism?
Albinism results from a genetic change, that leads to a reduced or lack of melanin production in the body and permanent changes in the structure of the eye before birth. Therefore albinism is a permanent condition, but with the use of vision aids, assistive technology and copious amounts of suncsreen, those with albinism lead normal lives.
People with albinism may have fair hair and skin, does albinism affect anything else?
Albinism does not affect any other part of the body, general health, intelligence or lifespan, other than the eye structures and usually the colouring of hair, skin and eyes. The biggest challenge for people with albinism is the range of eye conditions that reduce vision to varying degrees.
What are the eye conditions that people with albinism might have?
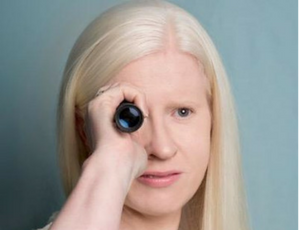
Those with albinism may have some or all of the following:
- Lack of visual clarity – they may not be able to see fine detail unless they are very close to an object.
- They may have a constant, involuntary movement of the eyeball called nystagmus, making it difficult to focus on moving objects.
- They may have reduced depth perception.
Their eyes may be very sensitive to light (photophobia), further reducing vision and causing pain . - In addition they often have other common eye conditions:
- They may be very far-sighted or near-sighted and may have other defects in the curvature of the lens of the eye (astigmatism).
- They may have problems in coordinating the eyes in fixing and tracking objects (strabismus), which may lead to an appearance of having “crossed eyes” at times.
Do all people with albinism have white hair or skin?
There are different clinical types of albinism, including Ocular Albinism (OA). Some types present with reduced melanin rather than lack of melanin. Ocular Albinism affects the eyes only and therefore people with this typing of the condition have seemingly “normal” pigmented hair and skin, not the stereotypical white hair and skin.
What is the life span of a person with albinism?
People with albinism live long, healthy lives just as anyone else, unless there is a separate medical condition. The biggest danger comes from skin cancer which develops more easily from unprotected sun exposure.
Further information is available in the members’ area of this site.





 Join us on Facebook
Join us on Facebook